Incidence of breast cancer has been increased obviously in Hong Kong. According to the report from Hong Kong Cancer Registry for Hospital Authority, the incidence of breast cancer increased from 2,962 cases in 2009 to 4,391 cases in 2017. The report also stated that breast cancer ranked no.3 in total incidence and ranked no.4(724 cases) in total mortality in 2017. Among the most common cancers in Hong Kong women, breast cancer ranked no.1 in incidence and ranked no.3 in mortality.
- Female
- Aged 50 or above. More than half of the breast cancer patients in Hong Kong are over aged 50. However, the incidence is also increased to patients who are aged 40 to 50
- First degree relatives who have been diagnosed breast or ovary cancer
- Never given birth or gives birth to her first child after the age of 35
- Early menarche before aged 12 or late menopause after aged 55
- With a past history of benign breast issues, non-invasive breast cancer, ovarian cancer, or endometrial cancer
- Taking hormonal replacement therapy
- Taking combined oral contraceptive pills
- Diet rich in animal fat
- Obesity after menopause
- Alcohol consumption
*The causes of breast cancer still not confirmed yet. Having the mentioned risk factors will not always directly result in breast cancer. According to American College of Preventive Medicine, women aged 50 to 74 should have Mammography bi-annually. Early detection and early treatment are the main keys to fight against breast cancer.
- Breast
- Skin thickening or lumps appearing
- Changing in sharp or size
- Dimpling in skin
- Nipple
- Lumps appearing or thickening
- Retraction or inversion
- Bleeding (Not Common)
- Armpit
- Swelling or lumps appearing
- Mammography
- The mammography will be performed by radiographer. Each sides of breast will be taken imaging in 2 different views. Before the examination, radiographer will instruct patient to stand in front to the X-Ray machine and to take off their tops. The breast will be pressed between 2 plastic plates to flatten and spread the breast tissue for clear imaging. The level of radiation to be used is very low dose and patient may feel uncomfortable in few seconds during the breast compression.
- Ultrasound
- Ultrasound is using sound wave to build up a picture of breast tissue for any masses in breast. Health care professionals will apply lubricant jelly and the probe will be moving around on patient’s breast. Patients will not feel painful and it will take only a few minutes to complete the examination.
- Biopsy
The followings are the 3 different types of biopsy:
- Fine Needle Aspiration: It could be performed in out-patient clinic and it is a simple and quick procedure. Doctors will use a fine needle and syringe to aspirate cells from breast tissue to collect specimen for pathology testing. This procedure could exclude the fluid-filled benign cysts.
- Core Needle Biopsy: Core needle biopsy use a needle larger than fine needle. The procedure will conduct under local anesthesia. The breast tissue will examine under microscopy for any cancer cells.
- Excision Biopsy: Under local or general anesthesia, the whole mass from the breast will be removed for microscopic examination.
Some reports state that over diagnosis may occur in breast cancer screening and unnecessary worry and investigation may be induced. International Agency for Research of Cancer (IARC) believes that women in age 50 to 69 still can be benefited from breast cancer screening. Breast cancer screening could decrease incidence and mortality.
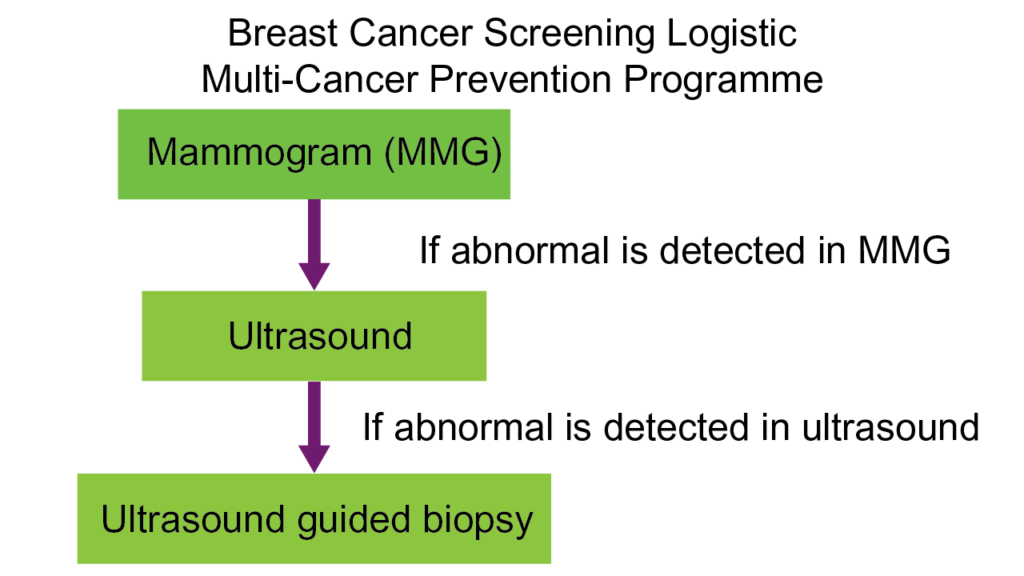
Step 1: Mammography
Mammography is the most common tool in breast cancer screening currently. It is mainly to detect any calcifications, lumps or masses in breast. Women aged 50 or above is recommended having mammography annually or bi- annually.
Step 2: Ultrasound
Ultrasound is a common supplementary examination. It could detect breast cancer that without calcification. Also, it is suitable for woman having high density breast. However, ultrasound could detect breast cancer with masses only therefore it could not be used as a replacement of mammography.
Step 3: Biopsy
If a mass detected under mammography or ultrasound, biopsy should be done to examine the suspected tissue cells. Under guided by ultrasound, a breast tissue specimen will be taken for microscopic examination.
Non-invasive Breast Cancer:
Carcinoma in situ/ Stage 0
Breast cancer cells are still in ductal or lobular and have not spared to other tissue. Cancer cells are not invasive in this stage.
Invasive Breast Cancer:
Stage 1:
Tumor size smaller than 2 cm. Axillary lymph node not affected. The cancer cells have not yet spread out.
Stage 2
Tumor size between 2 to 5 cm or lymph node affected or both appears at the same time. The cancer cells still not yet spread out.
Stage 3
Tumor size over 5 cm and lymph node affected but has not spread to distant organs.
Stage 4
Metastasis breast cancer with any size of tumors. Not only invade lymph nodes, cancer cells spread over the body.
The treatment plan depends on different factors, e.g. the stage of cancer, the growth rate and the size of the tumor, age and general health condition of the patient etc.
The major breast cancer treatments including:
- Surgery
- The area of breast excision will depend on the size of tumor, natural of tumor and level of metastasis. For breast cancer in early stage, the successful rate between lumpectomy (removal of tumor and surrounding tissue) with radiotherapy and total mastectomy (removal of whole breast) is almost the same.
- Radiotherapy
- Radiotherapy generally be conducted after surgery. In radiotherapy, high energy of radiation will be applied to non-invaded breast tissue to make sure all remaining cancer cells are eliminated and thus reducing the risk of recurrent.
- Chemotherapy
- Chemotherapy is using cytotoxic medication to eliminate cancer cells. There have 2 different forms of medication available in chemotherapy: oral or intravenous injection.
- Cytotoxic medication will spread over the body through blood stream to interrupt breast cancer cells growth and duplication. However, cytotoxic medication cannot distinguish between cancer cells and normal cells. Therefore, normal cells will also be killed by cytotoxic drug.
- Targeted Therapy
- Targeted therapy attack cancer cells selectively by medication. It interrupts cells from transmitting message for abnormal growth and hence, inhibit the growth and replication of tumor as well as the growth of new vessel while not damaging normal cells.
- Hormonal Therapy
- By controlling hormone level or preventing hormone provided nutrition to cancer cells, it could decrease or stop the growth of breast cancer cells.
- Regular breast check-up. Regular mammography over aged 50.
- Balance diet: High fiber and low fat.
- Average in body weight. Daily exercise at least 30 minutes.
- Restrict alcohol beverage consuming
- No smoking
